Shingles
Shingles is a painful skin rash with blisters but is not a life-threatening condition. It is caused by the varicella-zoster virus, the same virus that causes chickenpox.
Causes & Symptoms
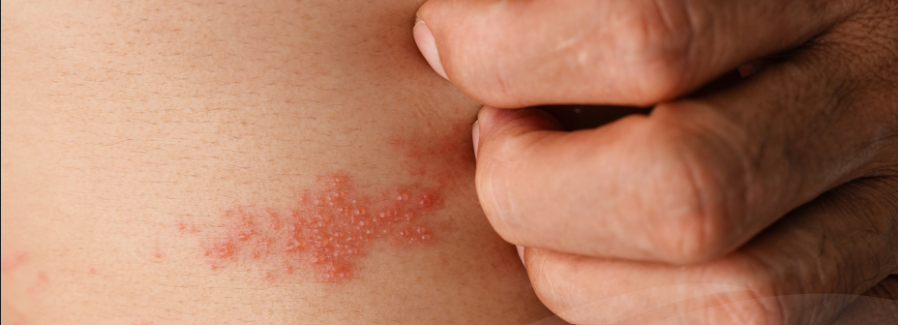
Shingles is caused by the varicella-zoster virus — the same virus that causes chickenpox. Anyone who’s had chickenpox may develop shingles. After you recover from chickenpox, the virus enters your nervous system and lies dormant for years.
Eventually, it may reactivate and travel along nerve pathways to your skin — producing shingles. But, not everyone who’s had chickenpox will develop shingles. The reason for shingles is unclear. But it may be due to lowered immunity to infections as you grow older. Shingles is more common in older adults and in people who have weakened immune systems.
The signs and symptoms of shingles usually affect only a small section of one side of your body. These signs and symptoms may include:
- Pain, burning, numbness or tingling
- Sensitivity to touch
- A red rash that begins a few days after the pain
- Fluid-filled blisters that break open and crust over
- Itching
Some people also experience:
- Fever
- Headache
- Sensitivity to light
- Fatigue
Pain is usually the first symptom of shingles. For some, it can be intense. Depending on the location of the pain, it can sometimes be mistaken for a symptom of problems affecting the heart, lungs or kidneys. Some people experience shingles pain without ever developing the rash. Most commonly, the shingles rash develops as a stripe of blisters that wraps around either the left or right side of your torso. Sometimes the shingles rash occurs around one eye or on one side of the neck or face.

Populations at risk
Being older than 50.
Shingles is most common in people older than 50. The risk increases with age.
Having certain diseases.
Diseases that weaken your immune system, such as HIV/AIDS and cancer, can increase your risk of shingles.
Undergoing cancer treatments.
Radiation or chemotherapy can lower your resistance to diseases and may trigger shingles.
Taking certain medications.
Drugs designed to prevent rejection of transplanted organs can increase your risk of shingles — as can prolonged use of steroids, such as prednisone.
When to see a doctor
Contact your doctor promptly if you suspect shingles, but especially in the following situations:
- The pain and rash occur near an eye. If left untreated, this infection can lead to permanent eye damage.
- You’re 60 or older, because age significantly increases your risk of complications.
- You or someone in your family has a weakened immune system (due to cancer, medications or chronic illness).
- The rash is widespread and painful.
Complications from shingles are possible and can include:
Postherpetic neuralgia
For some people, shingles pain continues long after the blisters have cleared. This condition is known as postherpetic neuralgia, and it occurs when damaged nerve fibers send confused and exaggerated messages of pain from your skin to your brain.
Vision loss
Shingles in or around an eye (ophthalmic shingles) can cause painful eye infections that may result in vision loss.
Neurological problems
Depending on which nerves are affected, shingles can cause an inflammation of the brain (encephalitis), facial paralysis, or hearing or balance problems.
Skin infections
If shingles blisters aren’t properly treated, bacterial skin infections may develop.
Treatment
There’s no cure for shingles, but prompt treatment with prescription antiviral drugs can speed healing and reduce your risk of complications. These medications include:
- Acyclovir (Zovirax)
- Famciclovir
- Valacyclovir (Valtrex)
Shingles can cause severe pain, so your doctor also may prescribe:
- Capsaicin topical patch (Qutenza)
- Anticonvulsants, such as gabapentin (Neurontin)
- Tricyclic antidepressants, such as amitriptyline
- Numbing agents, such as lidocaine, delivered via a cream, gel, spray or skin patch
- Medications that contain narcotics, such as codeine
- An injection including corticosteroids and local anesthetics
Shingles generally lasts between two and six weeks. Most people get shingles only once, but it is possible to get it two or more times.
Prevention
A shingles vaccine may help prevent shingles. People looking to receive the shingles vaccine have two options: Shingrix and Zostavax.
- Shingrix is approved and recommended for people age 50 and older, including those who’ve previously received Zostavax or had shingles.
- Zostavax has been shown to offer protection against shingles for about five years. It’s a live vaccine given as a single injection, usually in the upper arm. Zostavax is recommended for people age 60 and older. While it is no longer being sold in the U.S. as of July 2020, other countries may still use it.
The most common side effects of either shingles vaccine are redness, pain, tenderness, swelling and itching at the injection site, and headaches.
The shingles vaccine doesn’t guarantee that you won’t get shingles. But this vaccine will likely reduce the course and severity of the disease and reduce your risk of postherpetic neuralgia.
The shingles vaccine is used only as a prevention strategy. It’s not intended to treat people who currently have the disease. Talk to your doctor about which option is right for you.
Vaccination
Vaccines can help reduce the risk of shingles. Early treatment can help shorten a shingles infection and lessen the chance of complications. The most common complication is postherpetic neuralgia, which causes shingles pain for a long time after your blisters have cleared.
Cost: The vaccine is not provided for free in BC, with rare exception. It can be purchased at some pharmacies and travel clinics. Call ahead to ask about vaccine availability and cost. Some health insurance plans may cover the cost of the vaccine; check with your insurance provider. If you are covered by First Nations Health Benefits, please read the following.

